'Earliest Known Human Ancestor' Discovered, Scientists Claim
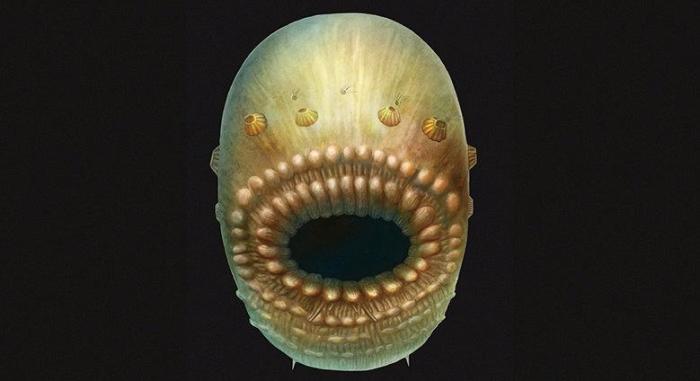
Scientists claimed to have discovered the earliest known human ancestor, in the face of a 540-million-year-old microscopic sea animal, which they said was part of the long evolutionary path that led to fish to mammals and humans.
"To the naked eye, the fossils we studied look like tiny black grains, but under the microscope the level of detail was jaw-dropping," Prof. Simon Conway Morris, from the University of Cambridge, told BBC News.
"We think that as an early deuterostome this may represent the primitive beginnings of a very diverse range of species, including ourselves. All deuterostomes had a common ancestor, and we think that is what we are looking at here."
An international team of researchers from the U.K., China and Germany carried out the study, which was published online in the Nature journal.
The journal explains that the discovery, named Saccorhytus, was the size of one millimeter, and is believed to have lived on the sea bed.
It is the most primitive example of the "deuterostomes" category of animals, which are believed to be the common ancestors of a number of species, including vertebrates, or backboned animals.
The ancient fossil was found in Shaanxi Province in China, and is at least 20 million years older than the previously discovered deuterostome groups, dating back between 510 to 520 million years ago.
"Saccorhytus now gives us remarkable insights into the very first stages of the evolution of a group that led to the fish, and ultimately, to us," said paleontologist Degan Shu of Northwest University in Xi'An.
What the scientists are calling a human ancestor apparently was covered with thin flexible skin and muscles, meaning that it moved around by contracting its muscles and wriggling.
Reuters noted that the creature's large mouth was striking in size, and it likely consumed food by engulfing particles or smaller creatures whole.
"The researchers found no evidence that it had an anus, meaning that its waste material may have been expelled out of the mouth. Conway Morris said that process 'from our perspective sounds rather unappealing,'" the report added.
Morris also said that humans appeared about 200,000 years ago on the evolutionary time scale, and suggested that more research remains to be undertaken on our "deeper ancestors."
Some Young Earth Creationists, such as Answers in Genesis' Ken Ham, have been very vocal in their opposition to such conclusions, however.
Ham has been warning against society's acceptance of evolution for years, and argued that the book of Genesis in the Bible is not poetical in nature, but the complete truth of how humans and other animals came to be on earth.
"Genesis is not written as poetry — it's historical narrative — the account of the only 100% true and reliable history of the earth and the universe," Ham wrote in a Facebook post on Tuesday.
"Every single biblical doctrine of theology ultimately directly or indirectly is founded in the first 11 chapters of Genesis," he claimed.
"Christians who believe in evolution are really attacking the character of God and undermining the authority of His Word — they need to repent."















![[Ready to PUB] Christian psychologist: Kids must develop 'resilience' to fulfill God's purpose for them](https://cdn.christianpost.com/images/cache/thumbnail/25/92/259219_a_300_200_658_146.jpg)











